Bacterial spot
Disease
Bacterial spot
Xanthomonas campestris pv. pruni (Smith)
Xanthomonadales
Distribution: This phytopathogenic bacterium can cause disease in trees like Prunus, hazelnut and walnut.
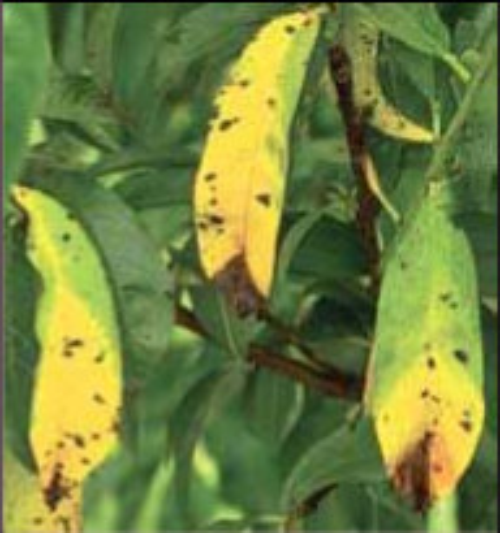
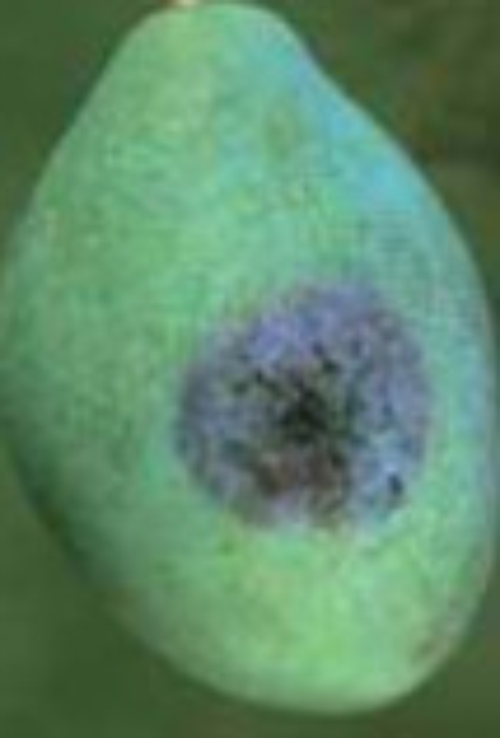
Bacterial spot appears on apricot, peach, nectarine, plum and prune. Brown, angular spots are typically concentrated along midribs and at the tips of leaves, where lesions may coalesce and cause a firing of leaf tips. Early leaf yellowing and drop occur following severe outbreaks of infection.
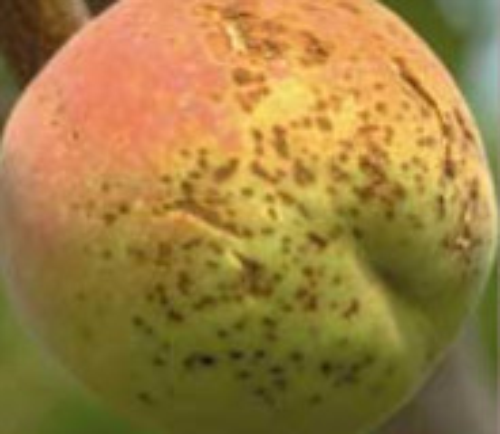
Fruit develop small, brown (purple in plum), sunken spots, usually on the exposed side. Sunken areas crack and coalesce to affect large areas of the fruit. Lesions on young fruit may exhibit deep pits with gumming; those on older fruit tend to be superficial.
Infection of new shoot growth can result in the production of elliptical cankers in the summer or the following spring. Summer cankers are usually located between the nodes; spring cankers tend to be located at nodes.






 Print
Print Email
Email