Flatheaded appletree borer
Insect
Flatheaded appletree borer
Chrysobothris femorata (Olivier)
Coleoptera: Buprestidae
Distribution: Most fruit-growing states and provinces in eastern North America.
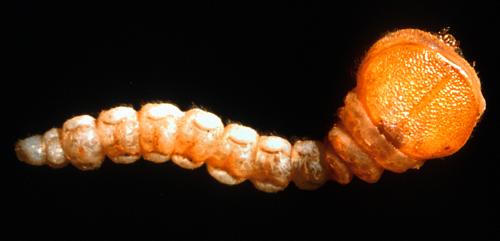
The adult is a short-horned beetle, flattened above, with short antennae and large conspicuous eyes (A). The upper surface of the body is dark metallic brown with slightly patterned wing covers. Underneath the wing covers (as seen in flight), the body is a bright metallic blue. The beetle's undersurface is coppery bronze. The larva (B) is light yellow and has a characteristic enlargement of the thoracic segments (just behind the head), which gives this insect its common name.





 Print
Print Email
Email