Drainage Workshop Impacts Local Farm Operations
MSU Extension Specialist, Ehsan Ghane, hosts a drainage workshop
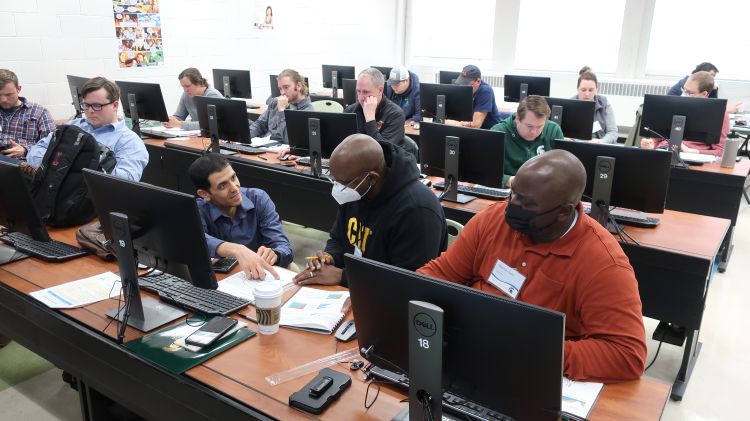

Protecting water quality and designing drainage systems to complement crop production is the goal of the Drainage Workshop hosted by MSU Extension. MSU Extension Specialist, Ehsan Ghane, hosted this event earlier this year in March 2022. Over the course of the 3-day event, participants learned the basics of water movement through the soil. Then, they learned how to design a drainage system including drainage layout, pipe sizing, and cost estimates.

In the 2022 Drainage Design Workshop, participants had the opportunity to try drainage design tools for themselves. Multiple design software's were demonstrated by various professionals in the industry. There was a demonstration of the user-friendly Drain Spacing Tool to maximize economic return on investment in the drainage system, taught by Ehsan Ghane, a demonstration of Global Mapper software as an aid in drainage design, taught by Will Word, and a demonstration of WATERCOURSE Water Management Design Tool as a drainage design software, taught by Nate Cook. Participants gained hands-on experience using WM-Subsurface Software for drainage design, taught by Joey Schlatter. Some of the drainage modeling tools, like the Drain-Spacing Tool, use weather data from the previous 30 years to maximize the profit and yield of a drainage system. Ghane said the next version of the Drain-Spacing Tool will include future climate scenarios to help account for more variable weather patterns.
The Drainage Design workshop was hosted in partnership with Michigan Land Improvement Contractors Association. At the conclusion of the 2022 event, 14 out of 20 (70%) of respondents said they plan on changing their operation because of the workshop and 17 respondents said they expect to gain an average $16/acre increased income because of the workshop.

Regarding Ghane's research, his team has been collecting flow and water-quality data since the year 2019, which has shown that controlled drainage and saturated buffers are effective in reducing drainage discharge and nitrate load. With the continuation of data collection, phosphorus removal can be evaluated. Other stakeholders funding the various drainage projects are the Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (MDARD); the Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE);, Michigan Alliance for Animal Agriculture; and the Corn Marketing Program of Michigan.



 Print
Print Email
Email