Tomato spotted wilt virus symptoms in chrysanthemum
Symptoms of tomato spotted wilt virus on chrysanthemum are yellow blotching and rings, necrotic lesions and stem collapse.
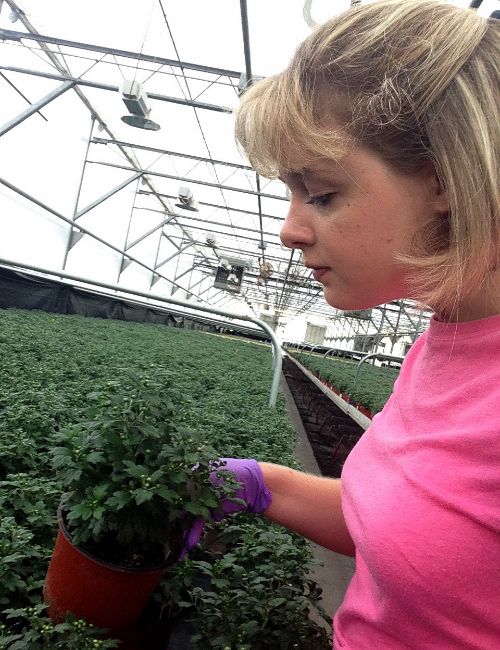

Growers should be scouting their chrysanthemums for symptoms of tomato spotted wilt virus. So far in 2016, tomato spotted wilt virus has been detected on five cultivars in chrysanthemum crops in multiple greenhouses. Tomato spotted wilt virus, a tospovirus, is vectored in the greenhouse by western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis).
Tomato spotted wilt virus symptoms
The symptoms of tomato spotted wilt virus are yellow blotching or rings, brown necrotic spotting, and graying and collapsing of stems, often directly under the flower. Growers should look for these symptoms when scouting:
- Blotchy chlorosis in circular patterns and angular necrosis.
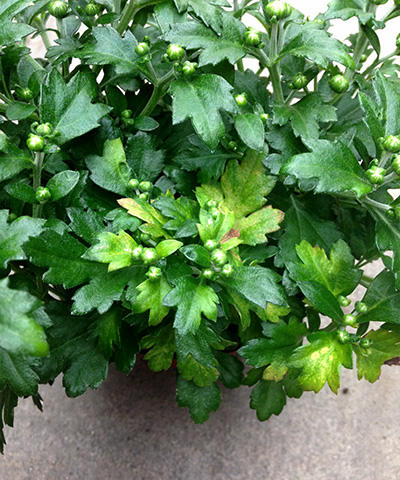

- Blotchy chlorosis on one branch of mum with circular chlorotic spots on leaves on lower foliage.

- Angular necrosis of leaves and plant stunting.

- Even yellow, chlorotic blotching on leaves

- Angular marginal necrosis and yellow rings around necrotic region.

Testing and managing tomato spotted wilt virus
Symptoms may initially appear on a few leaves or on one branch of the plant and some cultivars may show symptoms of the virus more readily than others. Growers will not be able to visually identify the virus, as it has similar symptoms to other viruses and other pathogens. Therefore, growers will need to submit samples to MSU Diagnostics Services or perform in-house testing to verify that the suspected plants do have tomato spotted wilt virus.
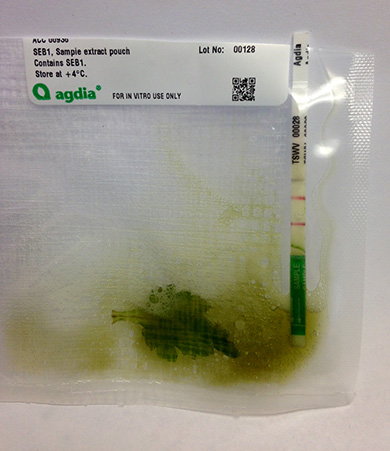
Chrysanthemum leaf positive for tomato spotted wilt virus.
Managing thrips is essential for preventing the spread of tomato spotted wilt virus because only thrips can spread the virus. Michigan State University Extension recommends the following products for thrips control.
Products for controlling thrips | |
|---|---|
|
Insecticide |
Group number |
|
Aria |
9C Flonicamid |
|
Mainspring |
28 |
|
Mesurol |
1A Carbamates |
|
Orthene 97 |
1B Organophosphate |
|
Overture |
Pyridalyl |
|
Pedestal |
15 Benzoylureas |
|
Pylon |
Chlorfenapyr |
|
Rycar |
UN |
As a guideline: 10 thrips per card are considered a very low population, while 100 per card are enough that some leaf or flower injury is likely. We do not know how many thrips it takes to move tomato spotted wilt virus through a greenhouse, and it probably depends on how many infected plants are present. However, if infected plants are present, even 30 thrips per card could spread the virus. When tomato spotted wilt virus has been spotted in the greenhouse, we recommend growers remove infected plants and keep the populations of thrips under 30 thrips per card per week.
Growers should immediately remove plants with symptoms and reduce thrips populations by spraying once every four to five days with one of the insecticides listed above, until thrips become hard to find. Growers should also follow label instructions and rotate modes of action as indicated by their group number or chemical class.
Mums safe for pollinators
For growers that want to provide garden centers with mums safe for pollinators, avoid spraying any insecticides when flowers are present that will still be there when plants are shipped to garden centers. The only products safe for bees are B.t., horticultural oil and insecticidal soap. However, soap and oil can injure mums and should not be sprayed at concentrations above 2 percent for soap or 1 percent for oil.
For more information, check out:
- Growers of fall garden mums need to inspect and test for tomato spotted wilt virus now
- How to manage plant viruses in the greenhouse
- Tomato spotted wilt virus
Note: Reference to commercial products or trade names does not imply endorsement by MSU Extension or bias against those not mentioned.



 Print
Print Email
Email

