Needlecast management
Editor’s note: This article is from the archives of the MSU Crop Advisory Team Alerts. Check the label of any pesticide referenced to ensure your use is included.
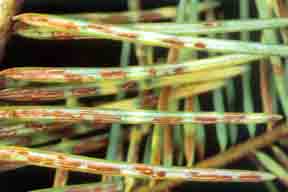
This is a good time to point out the fungal pathogens that cause Rhabdocline and Swiss needle cast of Douglas fir and Rhizosphaera needle cast of spruce will begin their yearlong infection of the 2010 needles unless you begin your spray programs. For these diseases to initiate infection, two events must occur, and they are happening right now.
First,
bud break and shoot elongation must be occurring. Second, the spores of
the fungus must be released from last year's infected needles. These
spores will ride to the new needles on rain-soaked pathways where the
pathogens will begin their infection process. So bud break, spore
release and rain lead to needle cast infections in Douglas fir and blue
spruce, and that is happening right now in most of the Christmas tree
plantations growing Douglas fir and spruce.
Since
the materials that work on Rhabdocline are effective on the Swiss needle
cast pathogen, you will get control of two diseases for the price of
one. Always follow label instructions when spraying. The most effective
material for control of Swiss and Rhabdocline is chlorothalonil.



 Print
Print Email
Email