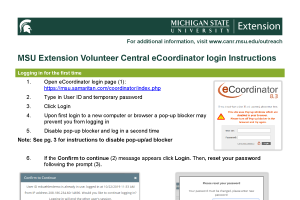
Understanding the different ways to pay for higher education
What you need to know about the different ways to pay for higher education, including work studies, student loans, grants and scholarships.
The cost of attending an institute of higher education can be pricey – this can include certificate programs as well as apprenticeships. Some young people assume all the money they receive to attend an institute of higher education does not have to be paid back. This is false. 4-H has activities that can help young people understand the types of funding available as well as if the money has to be paid back or not.
- Work study: A federal student aid program that provides part-time employment while you are enrolled in school to help pay your education expenses. Money awarded through a work study does not have to be paid back.
- Federal student loan: A loan funded by the federal government to help pay for your education. A federal student loan is borrowed money you must repay with interest.
- Grants: Financial award that does not have to be paid back. An example is the Federal Pell Grant. The maximum award for a Pell grant is $5,775. The amount you get, though, will depend on your financial need, cost of attendance, status as a full-time or part-time student, and plans to attend school for a full academic year or less.
- Scholarships: Financial awards from a college, trade school, foundation, business, organization, etc. The amount money ranges based on who is awarding the scholarship, and the criteria will vary from one scholarship to the next. A scholarship does not have to be paid back.
Build Your Future, a National 4-H curriculum written by Michigan State University Extension 4-H staff, has a lesson devoted to funding a post-secondary education and understanding the above terms.



 Print
Print Email
Email