Common lambsquarters
August 21, 2015
Chenopodium album L.
Life cycle
Erect summer annual.

Common lambsquarters plant.
Leaves
Cotyledons are oblong, narrow and linear with no midvein and a dull green to gray cast. The first one or two leaf pairs are opposite; all remaining leaves are alternate. Mature leaves are highly variable, being triangle-, diamond- or lance-shaped and light green above with gray, mealy undersides. Lower leaves have a petiole and irregular wavy to shallowly toothed margins. Young or newly emerged leaves often have a gray, mealy coating on both surfaces.


Common lambsquarters cotyledons do not have midveins (left). Common lambsquarters leaf (right).
Stems
Erect, moderately branched central stem up to 6 feet in height. Mature stems are vertically grooved with red, purple or light green stripes.
Flowers and fruit
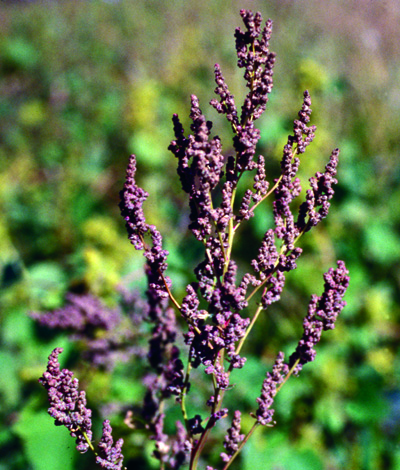
Green, inconspicuous flowers are found in dense, granular clusters at the stem ends. Round to oval, somewhat flattened, black to brown, shiny seeds are enclosed by a star-shaped, papery covering.

Mature seedhead of common lambsquarters.
Reproduction
Seeds.

Common lambsquarters seedling.
Similar weeds
Atriplex (Atriplex patula L.) Differs by having larger cotyledons, a more branching, spreading habit due to the opposite arrangement of the first several pairs of leaves and branches, and leaf bases with a lobe on each side.


Atriplex seedling (left). Atriplex leaf base with a lobe on each side (right).

Atriplex plant.
Print a PDF of this page: Common Lambsquarters.



 Print
Print Email
Email