Eastern black nightshade
August 7, 2015
Solanum ptycanthum Dun.
Life cycle
Erect, branching summer annual.

Young Eastern black nightshade plant.
Leaves
Seedlings have small, egg-shaped cotyledons with a pointed tip and a purplish tinge underneath followed by alternate, petiolated, simple leaves. First leaves are generally smooth, egg-shaped with wavy margins and a purplish tinge underneath; later leaves are slightly hairy, egg- to diamond-shaped with smooth to irregularly toothed margins.
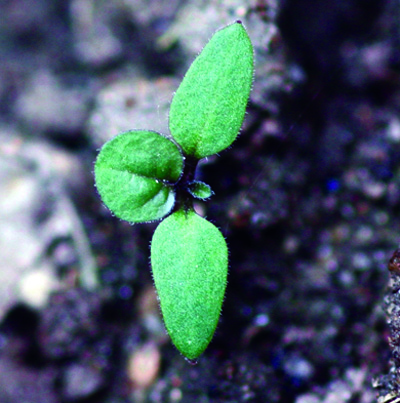

Eastern black nightshade seedling.


Upper leaf surface of Eastern black nightshade (left). Purplish lower leaf surface of Eastern black nightshade (right).
Stems
Erect and branching, up to 3-foot-tall stems with few hairs.
Flowers and fruit
Flowers are white to purple-tinged, star-shaped with five petals fused at the base surrounding five bright yellow anthers; found in downward facing clusters. Berries are glossy black at maturity and globe-shaped, and contain up to 110 seeds.

Eastern black nightshade mature berries.
Reproduction
Seeds.
Toxicity
All plant parts are toxic to animals.
Print a PDF of this page: Eastern black nightshade



 Print
Print Email
Email