Field violet
August 7, 2015
Viola arvensis Murr.
Life cycle
Prostrate to ascending winter annual.

Field violet plant.
Leaves
Young leaves that develop from a basal rosette are round to oval with a few shallow teeth on the margins, long petioles and small stipules. Mature leaves are longer and narrower with round-toothed margins, hairy veins on the leaf underside and large, deeply lobed stipules.
Stems
Prostrate to ascending, multi-branched stems are less than 16 inches long.
Flowers and fruit
Flowers have five white to pale yellow petals sometimes tinged with purple. The lower petal is the largest, and the sepals are the same length as the petals or slightly longer. Fruit are single-celled capsules with three valves.
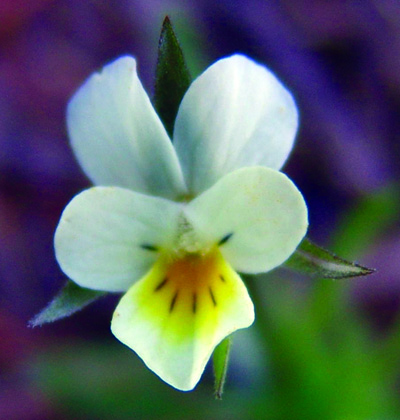

Field violet flower.
Reproduction
Seeds.
Similar weeds
Common blue violet (V. papilionacea Pursh) Differs by having a perennial nature with rhizomes; basal, hairless, heart-shaped leaves with round-toothed margins; and blue to purple to occasionally white flowers.


Common blue violet flower (left). Common blue violet foliage (right).
Print a PDF of this page: Field violet



 Print
Print Email
Email