Phytophthora
July 7, 2015
Root and stem rots
Pathogen
Phytophthora spp. (P. cactorum, P. drechsleri, P. nicotianae, etc.)
Hosts include
Achillea, Clematis, Euphorbia, Fragaria, Heuchera, Leucanthemum, Lilium, Phlox, Platycodon, Sedum, Sempervivum, Scabiosa and Viola.
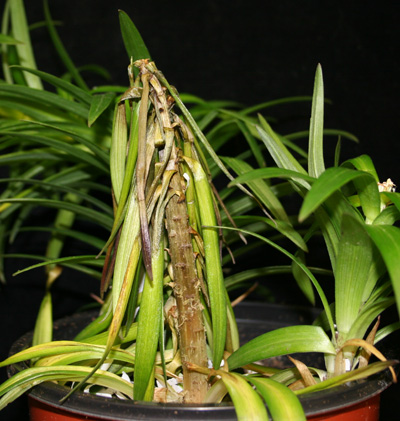

Aerial Phytophthora infection caused water-soaked lesions and stem collapse of lily
Symptoms
Stem and crown rot, root rot, stunting, wilting, yellowing. Infection of aboveground plant parts causes foliar dieback. Plants with low levels of infection may not have obvious symptoms.
Spread
Phytophthora is a soil-borne pathogen; spores can also be disseminated short distances through the air. Moving infested plant material can spread the disease. Phytophthora has several different spore types, including chlamydospores, sporangia, zoospores and oospores. (Refer to Pythium root rot for a description of these spore types.)
Management
Management strategies for Pythium spp. also apply to Phytophthora. Symptomatic plants should be removed and destroyed. Fungicides are often used to prevent losses. It is important to get good coverage of the affected plant parts. Fungicides have limited scope and should not be expected to cure heavily infected plants. Systemic fungicides should be used in rotation with protectant fungicides to delay resistance development. Applications at the high end of the labeled rate are required for Phytophthora control.

Discolored roots caused by Phytoph-thora infection.
Print a PDF of this page: Phytophthora



 Print
Print Email
Email