Pythium
July 7, 2015
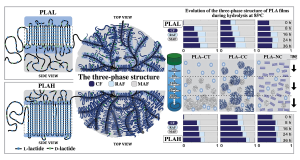
Root and stem rots
Pathogen
Pythium spp. (P. aphanidermatum, P. debaryanum, P. ultimum, etc.).
Hosts include
Berberis, Calendula, Chrysanthemum, Delphinium, Dianthus, Gaillardia, Gypsophila, Lathyrus, Lavandula, Lilium, Lupinus, Pelar-gonium, Phlox, Salvia, Sempervivum and Viola.
Symptoms
Wilting, stunting, uneven plant growth, crown rot and plant death. Roots are discolored. The cortex may slough off, leaving the vascular cylinder.
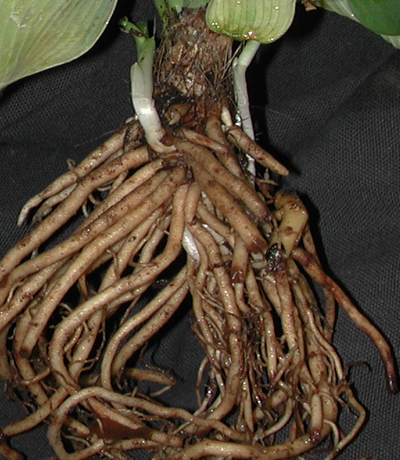

Small discolored lesions caused by Pythium sp. on the roots of a hosta.
Spread
Pythium spp. are soil-borne pathogens, so movement of infested soil or plant material can spread disease. This pathogen produces several types of spores, each with a slightly different function. Sporangia can either germinate and infect plants directly or produce many zoospores. Sporangia may be produced on both above- and below- ground plant parts. Zoospores are motile spores, which allow the fungus to spread in saturated soils or standing water. Each zoospore can cause a new infection. Oospores are thick-walled spores, which allow the fungus to survive on equipment or in soils for long periods of time. Disease can be quickly spread through recirculated irrigation water.

Infected roots are discolored. Note that the root cortex has sloughed off some of the roots.
Print a PDF of this page: Pythium



 Print
Print Email
Email