Begin managing white mold in soybeans this spring
White mold can be a damaging disease of Michigan soybeans. Consider implementing management practices this spring in fields prone to white mold.
Soybean producers should use an integrated approach to white mold management, and some of the most effective practices are implemented in the spring. This article discusses these practices and offers specific recommendations. An overarching concept to keep in mind when deciding which practices to implement is to select practices that have been proven to reduce white mold when it occurs but will not reduce yields significantly if environmental conditions don’t favor white mold.
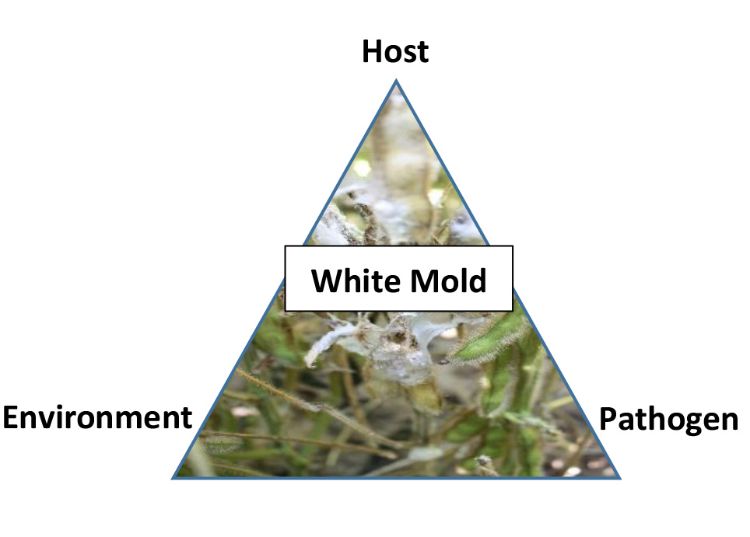
When managing white mold, it is helpful to understand principles of the disease triangle. White mold disease only occurs when all three factors come together: a susceptible host, presence of the pathogen and favorable weather conditions. By altering components of the triangle, which are discussed below, we can influence disease development including variety selection, affecting canopy microclimate through planting rate and row width, and even managing sclerotia of the pathogen.
Variety selection
Varieties vary significantly in their susceptibility to white mold and planting the most resistant varieties in fields prone to white mold is a key management practice. All seed company catalogs provide relative white mold ratings for the varieties they offer. These ratings provide valuable information when comparing varieties from a given seed company. However, they are less useful for comparing the level of white mold tolerance between varieties from different companies.
Selecting varieties that resist lodging and have a narrower canopy width can also reduce the incidence and severity of white mold. Planting varieties from a range of maturity groups may help some fields avoid severe white mold infestations by staggering the susceptible flowering period. We saw this in 2014 where the early maturing varieties tended to avoid white mold infection and development.
Planting rate
Reducing planting rates can be an effective tactic for reducing white mold. We saw this in two on-farm planting rate trials conducted in Michigan (Table 1). Reduced planting rates will decrease the potential for lodging and plant-to-plant spread of the disease. Consider reducing planting rates to end up with a harvest stand of 80,000 to 100,000 plants per acre in 30-inch rows when planting into fields having a high potential to develop white mold. There are many factors that determine final plant stands such as soybean germination and emergence that producers need to account for when reducing planting rates.
Emerson Nafziger and Dennis Bowman at the University of Illinois developed an excellent soybean planting rate calculator. The calculator allows users to fine-tune planting rates by entering the final stand they want to achieve and adjusting germination and emergence percentages for seed quality and planting conditions.
|
Table 1. Soybean planting rate effects on yield and income at the two locations infested with white mold. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Planting rate |
Yield (bushels per acre) |
Income ($ per acre) | ||
|
2015 Sanilac |
2018 Saginaw |
2015 Sanilac |
*2018 Saginaw | |
|
80,000 |
63.2 a |
66.2 a |
$622 |
$653 |
|
100,000 |
61.1 b |
66.5 a |
$591 |
$648 |
|
130,000 |
61.5 b |
64.3 a |
$582 |
$612 |
|
160,000 |
57.9 c |
61.2 b |
$531 |
$565 |
|
LSD0.10 |
1.7 |
2.4 |
|
|
*Using 2020 figures for seed cost ($62/140,000 seed unit) and market price ($10.40 per bushel).
Row spacing
Wide rows greater than 20 inches can decrease white mold but may not always lead to a yield increase. On-farm trials conducted in Michigan have shown that 30-inch rows reduce soybean yields by approximately 2 bushels per acre when compared to 15-inch rows.
Nutrient management
Applications of nitrogen fertilizers or manure have been shown to increase early plant growth and canopy closure, creating favorable conditions for the development of white mold. Therefore, nitrogen fertilizer and manure applications should be avoided in fields having a history of white mold. Nitrogen fertilizer applications to soybeans are rarely profitable, making this the easiest practice to implement.

Cover crops
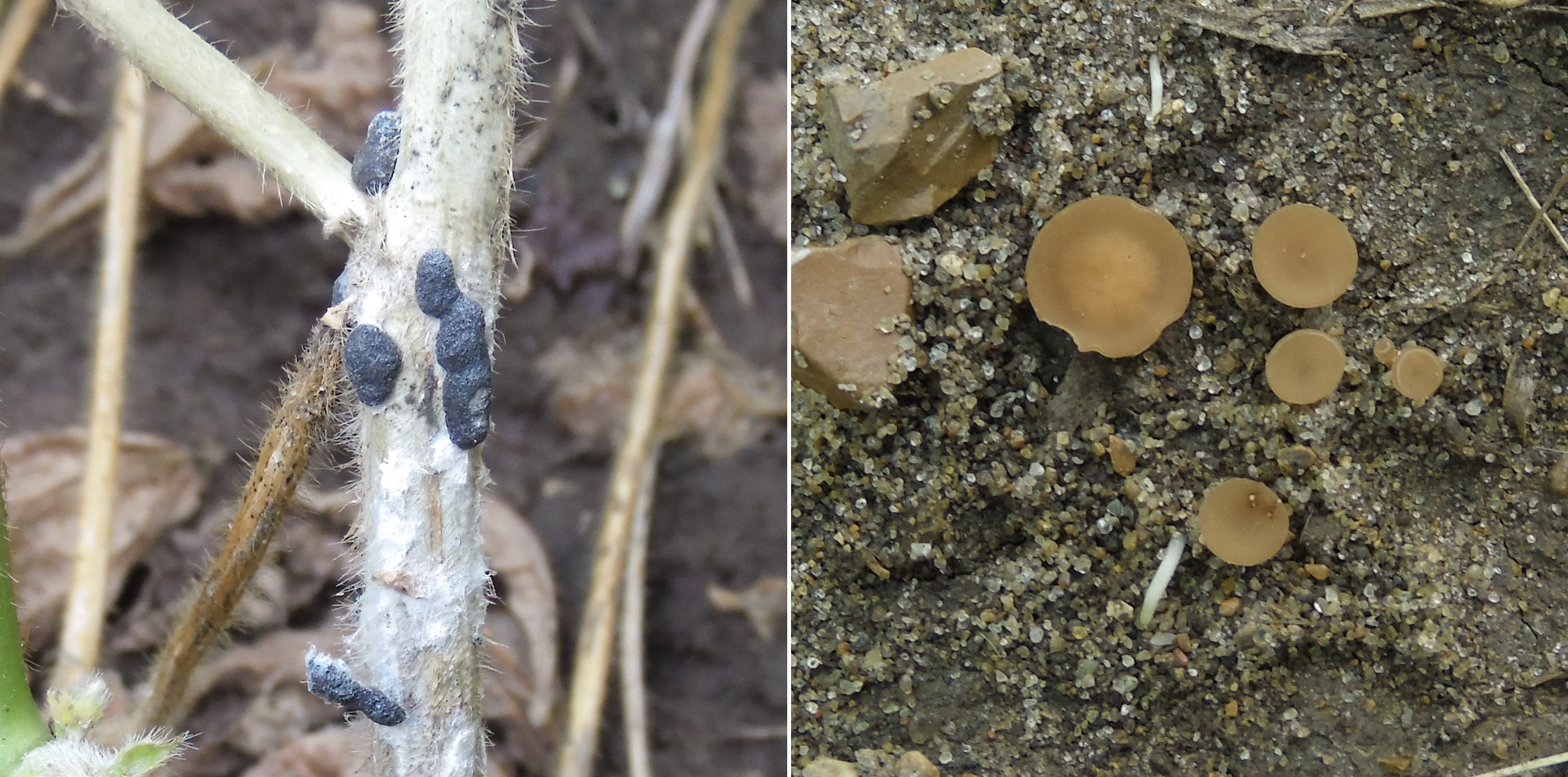
Using small grain cover crops like oat, wheat or cereal rye grown with soybean can stimulate sclerotia germination, apothecia emergence and spore release before soybean blossoms appear. This can potentially lower white mold incidence and protect yield. Crimping and rolling a cereal rye cover crop has also been shown to reduce white mold incidence. Cover crops will alter the environment, so manage them carefully.
Biological control
Producers may also consider applying a biological control product such as Contans to fields having a history of severe white mold. This product contains Coniothyrium minitans, a naturally occurring fungus that attacks and degrades sclerotia in the soil. The product should be incorporated into the soil as uniformly as possible to a depth of 2 inches at least three months prior to initial soybean bloom.
It is important to note that Contans will attack and degrade the sclerotia only when in contact with white mold sclerotia. Tillage operations deeper than 2 inches deep should be avoided following an application of Contans to prevent redistributing viable sclerotia into the top 2 inches where they can germinate and infect your soybean crop.
Remember, the most effective white mold strategies incorporate a variety of tactics and many of the most effective tactics are implemented prior to or at planting.
This article was produced by Michigan State University Extension and the Michigan Soybean Committee. It was originally published in the Spring 2021 issue of the Michigan Soybean News.



 Print
Print Email
Email