Morphological, barrier, thermal, and rheological properties of high-pressure treated co-extruded polylactide films and the suitability for food packaging
JasimAhmed; Mehrajfatema Z.Mulla; Sheikha A.Al-Zuwayed; AntonyJoseph; RafaelAuras
Food Packaging and Shelf Life; Volume 32, June 2022, 100812 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2022.100812
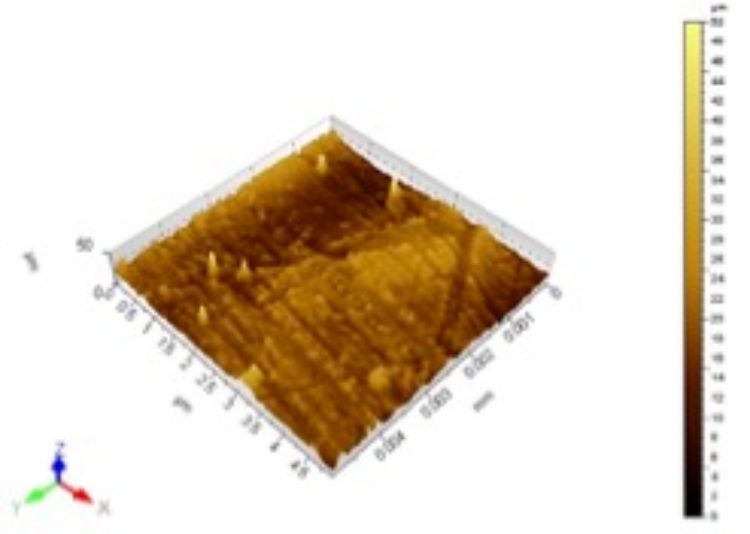
The objective of this study was to examine the influence of the HP-treatment in the pressure range of 300–600 MPa for a residence time of 15 min, and thereafter, assessed changes in the morphological, thermal, rheological, optical, and barrier properties of two commercial co-extruded polylactide films with varying thickness (25-μm and 75-μm). The barrier properties of the films remained unchanged by the treatment except for the thin film (25-μm) that was treated at 600 MPa. The surface morphology and roughness of the thin films were affected by the HP-treatment while XRD analysis confirmed changes in the structure/crystallinity of PLA. The TGA curves demonstrated a variation in thermograms between the two films. HP-treated films exhibited predominating liquid-like property on the melt, and the thin films exhibited higher mechanical rigidity than the thick films. The results demonstrated that HP-treatment significantly affected microstructures of the film. More studies are required for the commercial success of these films by improving film properties and the interaction between the film and the food under high-pressure.



 Print
Print Email
Email